Facebook published an internal memo today trying to minimize the morale damage of TechCrunch’s investigation that revealed it’d been paying people to suck in all their phone data. Attained by Business Insider’s Rob Price, the memo from Facebook’s VP of production engineering and security Pedro Canahuati gives us more detail about exactly what data Facebook was trying to collect from teens and adults in the US and India. But it also tries to claim the program wasn’t secret, wasn’t spying, and that Facebook doesn’t see it as a violation of Apple’s policy against using its Enterprise Certificate system to distribute apps to non-employees — despite Apple punishing it for the violation.
Here we lay out the memo with section by section responses to Facebook’s claims challenging TechCrunch’s reporting. Our responses are in bold and we’ve added images.
Memo from Facebook VP Pedro Canahuati
APPLE ENTERPRISE CERTS REINSTATED
Early this morning, we received agreement from Apple to issue a new enterprise certificate; this has allowed us to produce new builds of our public and enterprise apps for use by employees and contractors. Because we have a few dozen apps to rebuild, we’re initially focusing on the most critical ones, prioritized by usage and importance: Facebook, Messenger, Workplace, Work Chat, Instagram, and Mobile Home.
New builds of these apps will soon be available and we’ll email all iOS users for detailed instructions on how to reinstall. We’ll also post to iOS FYI with full details.
Meanwhile, we’re expecting a follow-up article from the New York Times later today, so I wanted to share a bit more information and background on the situation.

What happened?
On Tuesday TechCrunch reported on our Facebook Research program. This is a market research program that helps us understand consumer behavior and trends to build better mobile products.
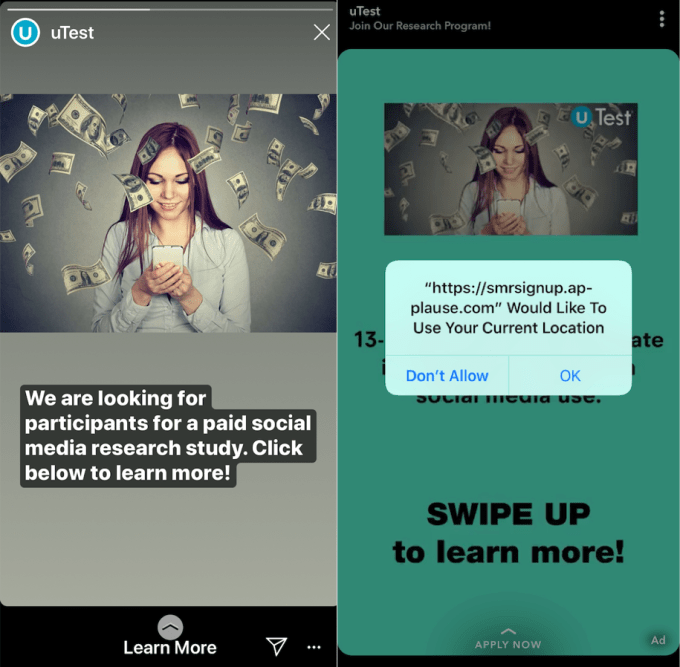
TechCrunch implied we hid the fact that this is by Facebook – we don’t. Participants have to download an app called Facebook Research App to be involved in the stud. They also characterized this as “spying,” which we don’t agree with. People participated in this program with full knowledge that Facebook was sponsoring this research, and were paid for it. They could opt-out at any time. As we built this program, we specifically wanted to make sure we were as transparent as possible about what we were doing, what information we were gathering, and what it was for — see the screenshots below.
We used an app that we built ourselves, which wasn’t distributed via the App Store, to do this work. Instead it was side-loaded via our enterprise certificate. Apple has indicated that this broke their Terms of Service so disabled our enterprise certificates which allow us to install our own apps on devices outside of the official app store for internal dogfooding.
Author’s response: To start, “build better products” is a vague way of saying determining what’s popular and buying or building it. Facebook has used competitive analysis gathered by its similar Onavo Protect app and Facebook Research app for years to figure out what apps were gaining momentum and either bring them in or box them out. Onavo’s data is how Facebook knew WhatsApp was sending twice as many messages as Messenger, and it should invest $19 billion to acquire it.
Facebook claims it didn’t hide the program, but it was never formally announced like every other Facebook product. There were no Facebook Help pages, blog posts, or support info from the company. It used intermediaries Applause (which owns uTest) and CentreCode (which owns Betabound) to run the program under names like Project Atlas and Project Kodiak. Users only found out Facebook was involved once they started the sign-up process and signed a non-disclosure agreement prohibiting them from discussing it publicly.
TechCrunch has reviewed communications indicating Facebook would threaten legal action if a user spoke publicly about being part of the Research program. While the program had run since 2016, it had never been reported on. We believe that these facts combined justify characterizing the program as “secret”

The Facebook Research program was called Project Atlas until you signed up
How does this program work?
We partner with a couple of market research companies (Applause and CentreCode) to source and onboard candidates based in India and USA for this research project. Once people are onboarded through a generic registration page, they are informed that this research will be for Facebook and can decline to participate or opt out at any point. We rely on a 3rd party vendor for a number of reasons, including their ability to target a Diverse and representative pool of participants. They use a generic initial Registration Page to avoid bias in the people who choose to participate.
After generic onboarding people are asked to download an app called the ‘Facebook Research App,’ which takes them through a consent flow that requires people to check boxes to confirm they understand what information will be collected. As mentioned above, we worked hard to make this as explicit and clear as possible.
This is part of a broader set of research programs we conduct. Asking users to allow us to collect data on their device usage is a highly efficient way of getting industry data from closed ecosystems, such as iOS and Android. We believe this is a valid method of market research.
Author’s response: Facebook claims it wasn’t “spying”, yet it never fully laid out the specific kinds of information it would collect. In some cases, descriptions of the app’s data collection power were included in merely a footnote. The program did not specify specific data types gathered, only saying it would scoop up “which apps are on your phone, how and when you use them” and “information about your internet browsing activity”
The parental consent form from Facebook and Applause lists none of the specific types of data collected or the extent of Facebook’s access. Under “Risks/Benefits”, the form states “There are no known risks associated with this project however you acknowledge that the inherent nature of the project involves the tracking of personal information via your child’s use of Apps. You will be compensated by Applause for your child’s participation.” It gives parents no information about what data their kids are giving up.
Facebook claims it uses third-parties to target a diverse pool of participants. Yet Facebook conducts other user feedback and research programs on its own without the need for intermediaries that obscure its identity, and only ran the program in two countries. It claims to use a generic signup page to avoid biasing who will choose to participate, yet the cash incentive and technical process of installing the root certificate also bias who will participate, and the intermediaries conveniently prevent Facebook from being publicly associated with the program at first glance. Meanwhile, other clients of the Betabound testing platform like Amazon, Norton, and SanDisk reveal their names immediately before users sign up.
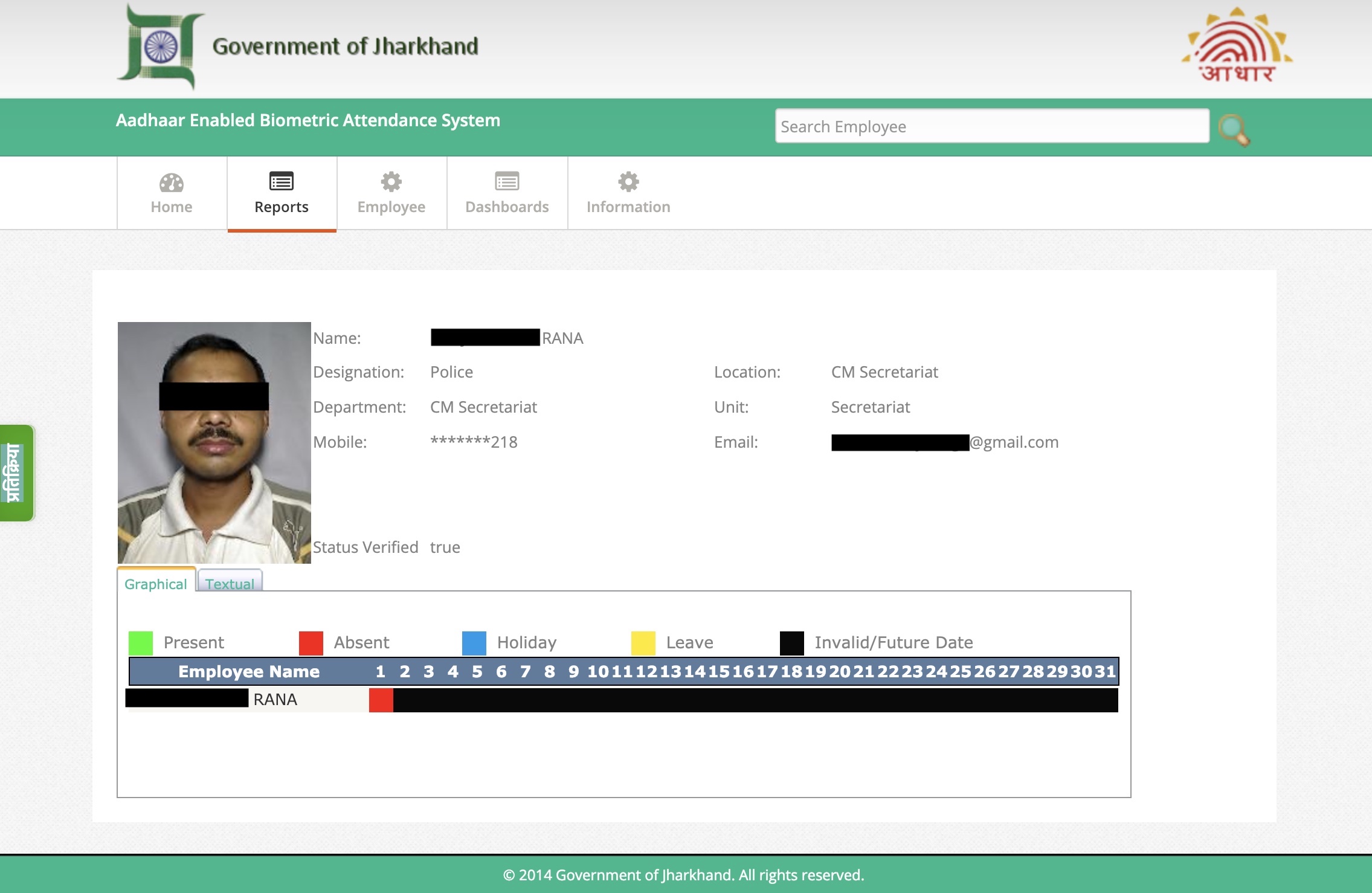
Facebook’s ads recruiting teens for the program didn’t disclose its involvement
Did we intentionally hide our identity as Facebook?
No — The Facebook brand is very prominent throughout the download and installation process, before any data is collected. Also, the app name of the device appears as “Facebook Research” — see attached screenshots. We use third parties to source participants in the research study, to avoid bias in the people who choose to participate. But as soon as they register, they become aware this is research for Facebook
Author’s response: Facebook here admits that users did not know Facebook was involved before they registered.
What data do we collect? Do we read people’s private messages?
No, we don’t read private messages. We collect data to understand how people use apps, but this market research was not designed to look at what they share or see. We’re interested in information such as watch time, video duration, and message length, not that actual content of videos, messages, stories or photos. The app specifically ignores information shared via financial or health apps.
Author’s response: We never reported that Facebook was reading people’s private messages, but that it had the ability to collect them. Facebook here admits that the program was “not designed to look at what they share or see”, but stops far short of saying that data wasn’t collected. Fascinatingly, Facebook reveals it was that it was closely monitoring how much time people spent on different media types.
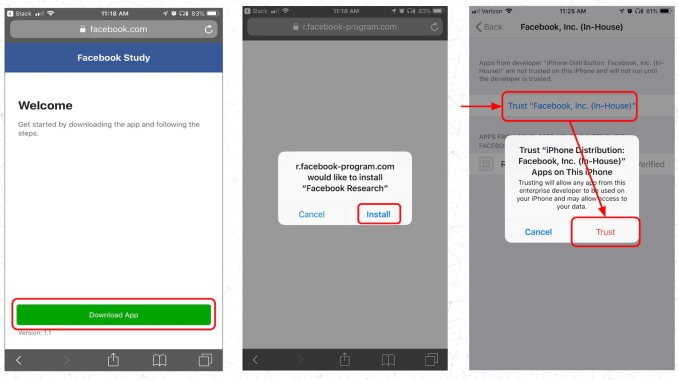
Facebook Research abused the Enterprise Certificate system meant for employee-only apps
Did we break Apple’s terms of service?
Apple’s view is that we violated their terms by sideloading this app, and they decide the rules for their platform, We’ve worked with Apple to address any issues; as a result, our internal apps are back up and running. Our relationship with Apple is really important — many of us use Apple products at work every day, and we rely on iOS for many of our employee apps, so we wouldn’t put that relationship at any risk intentionally. Mark and others will be available to talk about this further at Q&A later today.
Author’s response: TechCrunch reported that Apple’s policy plainly states that the Enterprise Certificate program requires companies to “Distribute Provisioning Profiles only to Your Employees and only in conjunction with Your Internal Use Applications for the purpose of developing and testing” and that “You may not use, distribute or otherwise make Your Internal Use Applications available to Your Customers”. Apple took a firm stance in its statement that Facebook did violate the program’s policies, stating “Facebook has been using their membership to distribute a data-collecting app to consumers, which is a clear breach of their agreement with Apple.”
Given Facebook distributed the Research apps to teenagers that never signed tax forms or formal employment agreements, they were obviously not employees or contractors, and most likely use some Facebook-owned service that qualifies them as customers. Also, I’m pretty sure you can’t pay employees in gift cards.

from TechCrunch https://tcrn.ch/2S2wIEU